Documentation
SECURETEA SECURE YOUR SYSTEM
The OWASP SecureTea Project is an application designed to help Secure a person’s laptop or computer / server with IoT (Internet Of Things) for notify users (via various communication mechanisms), whenever someone accesses their computer / server. This application uses the touchpad/mouse/wireless mouse to determine activity and is developed in Python and tested on various machines (Linux, Mac & Windows).
The purpose of this application is to warn the user (via various communication mechanisms) whenever their computer / server accessed. This small application was developed and tested in python in Linux machine, macOS & Windows.
Target User
It was written to be used by anyone who is interested in Security IoT (Internet of Things) and still needs further development.
How it functions
- Keep track of the movement of the mouse/touchpad
- Detect who access the laptop with mouse/touchpad is installed
- Send warning messages on Twitter/SMS/Slack/Telegram
Objective
To alert the user via variuos communication mechanism, whenever his/her laptop had been accessed by someone. And also it can be used to monitor your system.
Pre-requisites
Hardware
- Linux OS / Raspberry Pi - have
sudoaccess on the terminal/console - Mouse / Wireless Mouse / Touchpad congenital laptop
Software
- Python - https://www.python.org/ (
sudo apt-get install python) - Angular -
https://angular.io/ - A Twitter account -
https://twitter.com - Libnetfilter -
https://www.netfilter.org/projects/libnetfilter_queue/ - Yara
- Clam AV -
https://www.clamav.net/
Procedure for installing
You can install OWASP SecureTea Tool using the following methods:
Setting up a virtual environment
- Install virtualenv
pip install virtualenv - Create a virtual environment named
venv1
virtualenv venv1 - Activate virtual environment
venv1
source venv1/bin/activate
PyPi
You can install SecureTea from PyPi package manager using the following command:
$ sudo python3 -m pip install securetea
Please make sure all dependencies are installed if this fails.
GitHub
Installing from GitHub involves the following steps:
-
Clone the repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/OWASP/SecureTea-Project.git -
Navigate into the project directory:
$ cd SecureTea-Project -
Install Python dependencies:
$ sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt -
Install SecureTea package:
$ sudo python3 setup.py install
If done, proceed to After installation
Zip
Installing from Zip involves the following steps:
-
Download the zip.
-
Unzip using:
$ unzip master.zip -
Navigate into the project directory:
$ cd SecureTea-Project -
Install python dependencies
$ sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt -
Install SecureTea package
$ sudo python3 setup.py install
Tip: Incase of any error during installation related to NetfilterQueue, try using $ sudo apt-get install build-essential python-dev libnetfilter-queue-dev to resolve the error.
Configuring SecureTea
Editing the configurations using a text-editor
Default configuration:
{
"twitter": {
"api_key": "XXXX",
"api_secret_key": "XXXX",
"access_token": "XXXX",
"access_token_secret": "XXXX"
},
"telegram": {
"token": "XXXX",
"user_id": "XXXX"
},
"twilio": {
"twilio_sid": "XXXX",
"twilio_token": "XXXX",
"twilio_from": "XXXX",
"twilio_to": "XXXX"
},
"slack": {
"token": "XXXX",
"user_id": "XXXX"
},
"aws_ses": {
"aws_email": "XXXX",
"aws_access_key": "XXXX",
"aws_secret_key": "XXXX"
},
"gmail": {
"sender_email": "XXXX",
"to_email": "XXXX",
"password": "XXXX"
},
"firewall": {
"interface": "",
"inbound_IPRule": {
"action": "0",
"ip_inbound": ""
},
"outbound_IPRule": {
"action": "0",
"ip_outbound": ""
},
"protocolRule": {
"action": "0",
"protocols": "ICMP"
},
"scanLoad": {
"action": "0",
"extensions": ".exe"
},
"source_portRule": {
"action": "0",
"sports": ""
},
"dest_portRule": {
"action": "0",
"dports": ""
},
"HTTPRequest": {
"action": "0"
},
"HTTPResponse": {
"action": "0"
},
"DNSRule": {
"action": "0",
"dns": ""
},
"time": {
"time_lb": "00:00",
"time_ub": "23:59"
}
},
"insecure_headers": {
"url": ""
},
"ids": {
"threshold": 10,
"interface": "XXXX"
},
"server_log": {
"log_type": "",
"log_file": "",
"window": "30",
"ip_list": "",
"status_code": ""
},
"debug": false
}
Using gedit
gedit securetea.conf
Using vim
vi securetea.conf
Configuring using interactive setup mode
Setup all the features
- Start SecureTea without any parameters:
sudo SecureTea.py
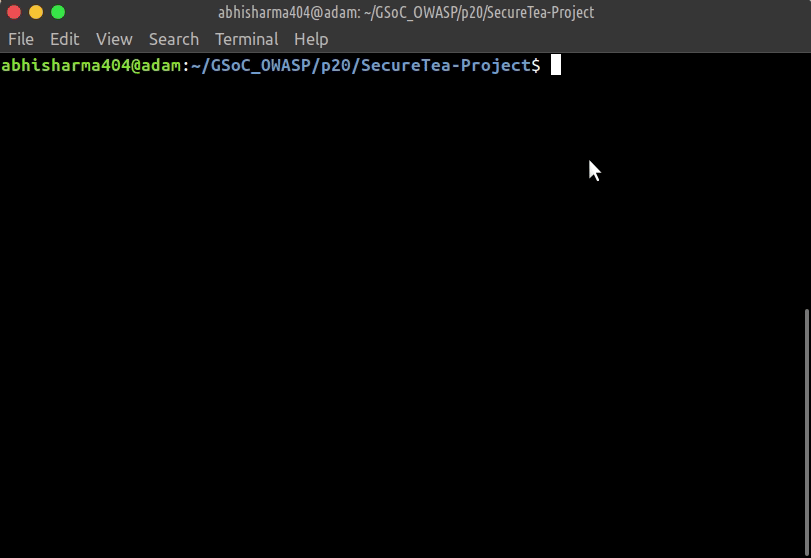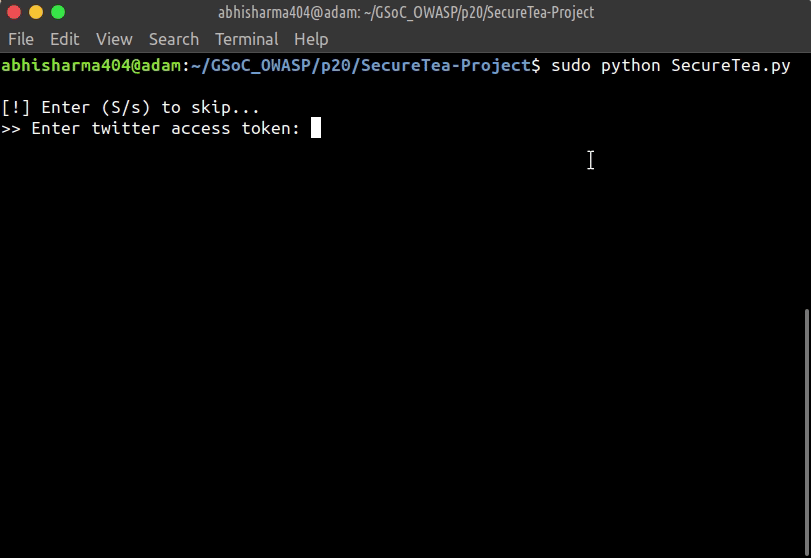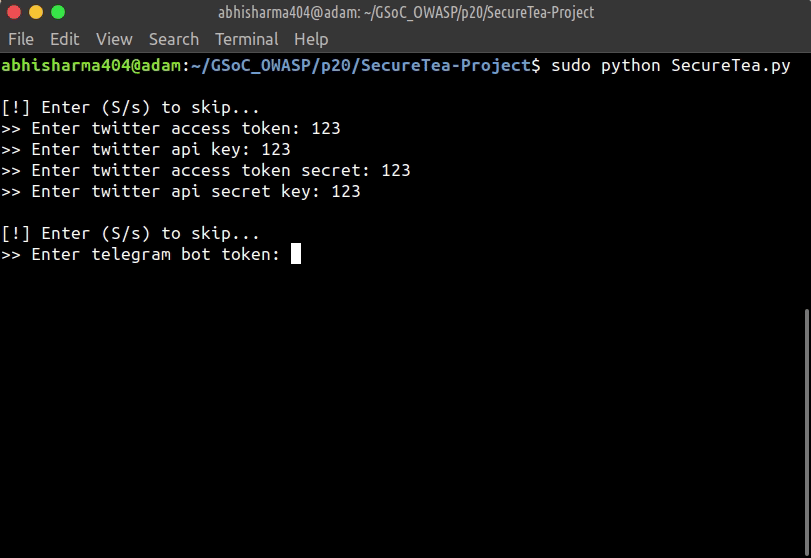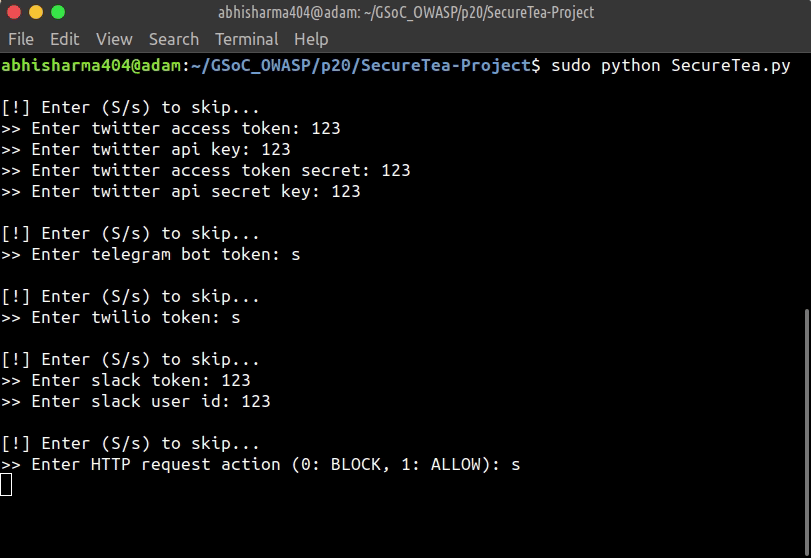
This will start an interactive setup mode, to skip a particular setup, enter s or S.
Setup a particular feature
Arguments list
--telegram Start Telegram interactive setup
--twitter Start Twitter interactive setup
--twilio_sms Start Twilio SMS interactive setup
--firewall Start Firewall interactive setup
--aws_ses Start Amazon Web Services(AWS-Simple Email Services) interactive setup
--gmail Start G-Mail interactive setup
Examples:
-
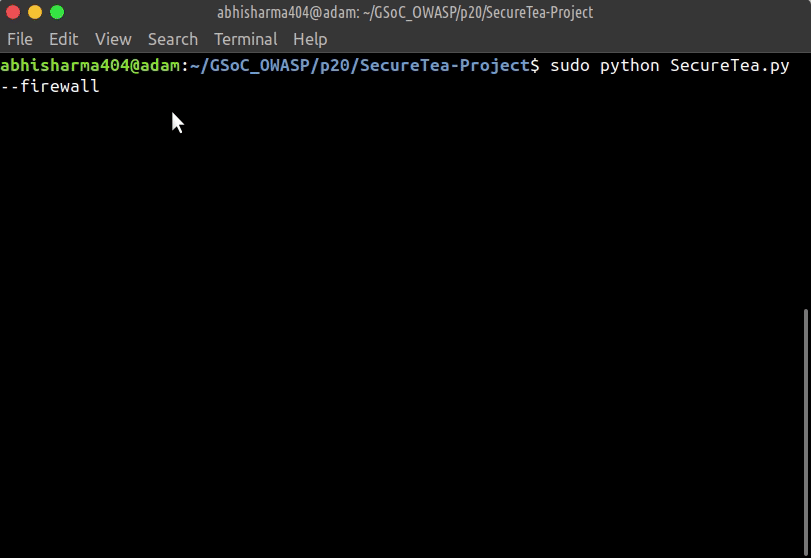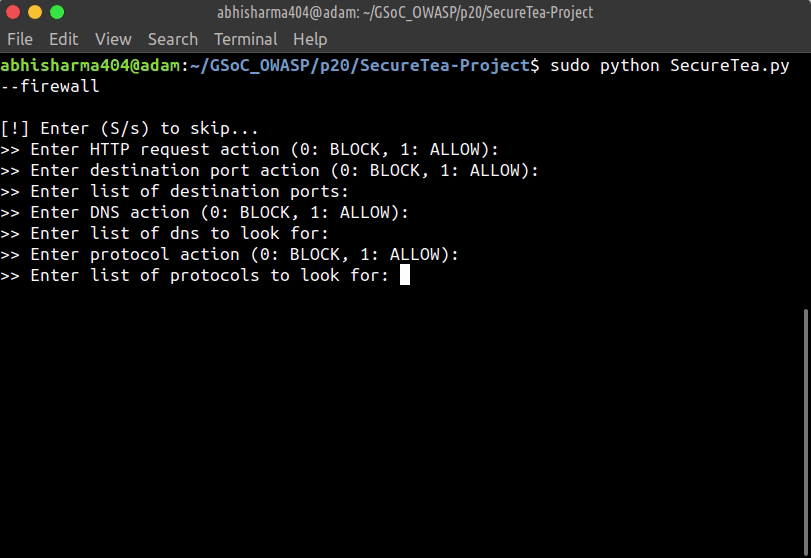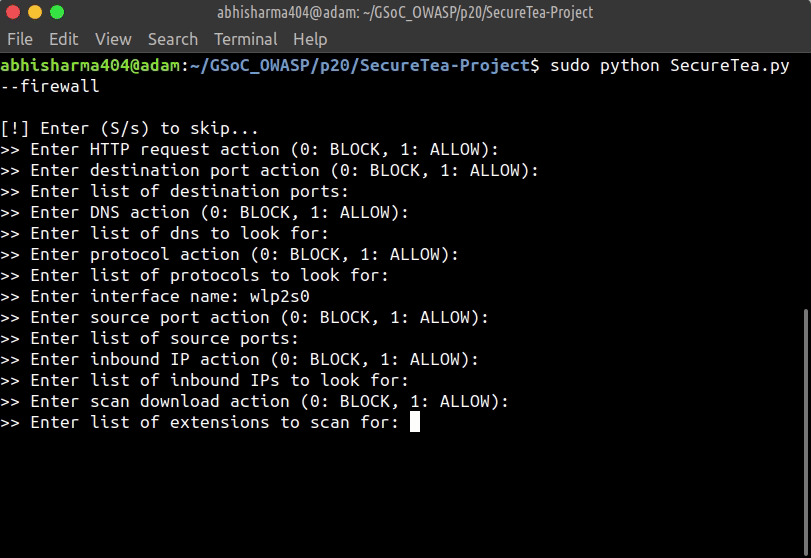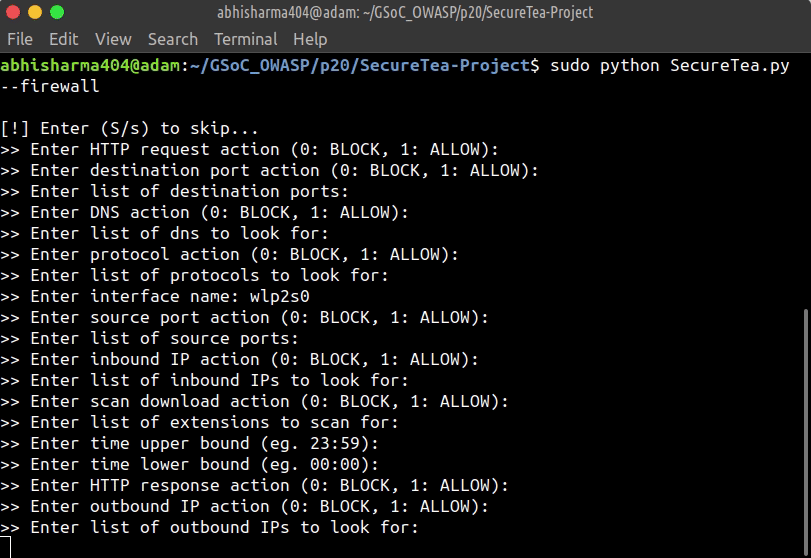
Starting SecureTea-Firewall interactive setup:
sudo SecureTea.py --firewall
-
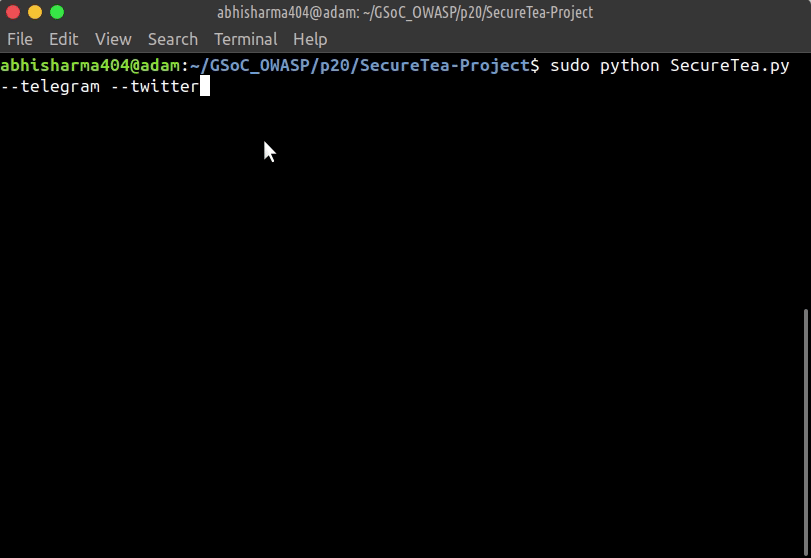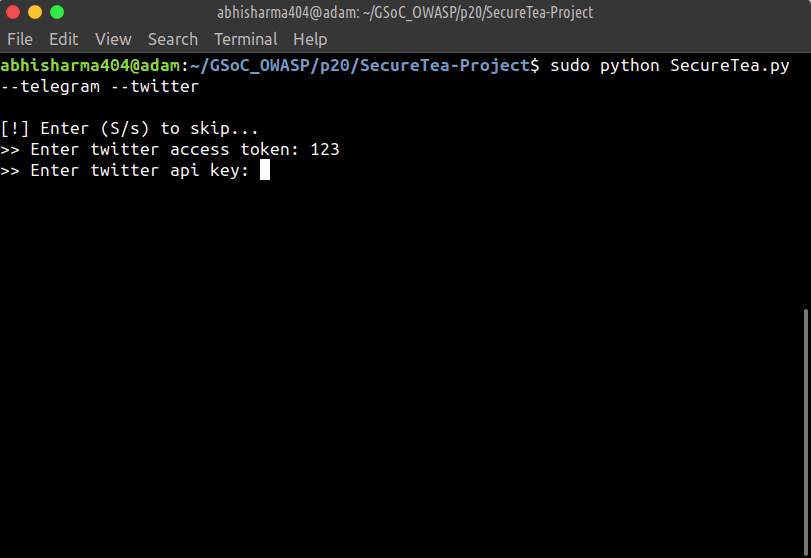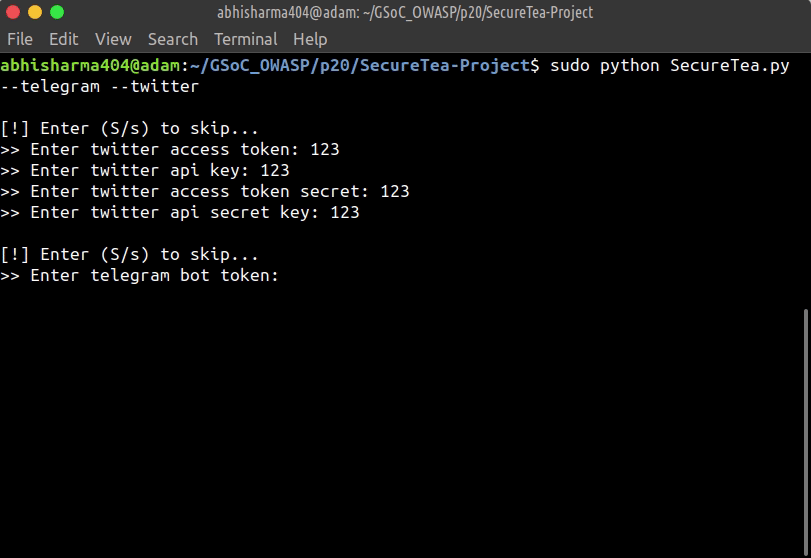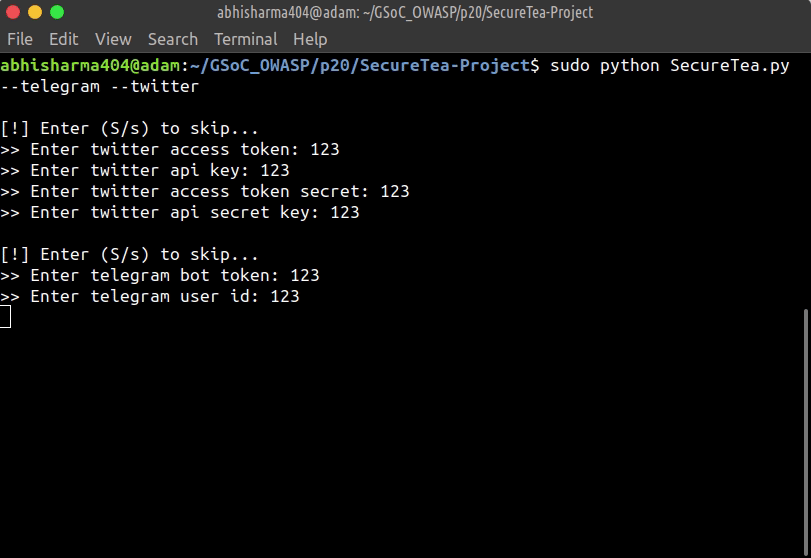
Starting Telegram & Twitter interactive setup:
sudo SecureTea.py --telegram --twitter
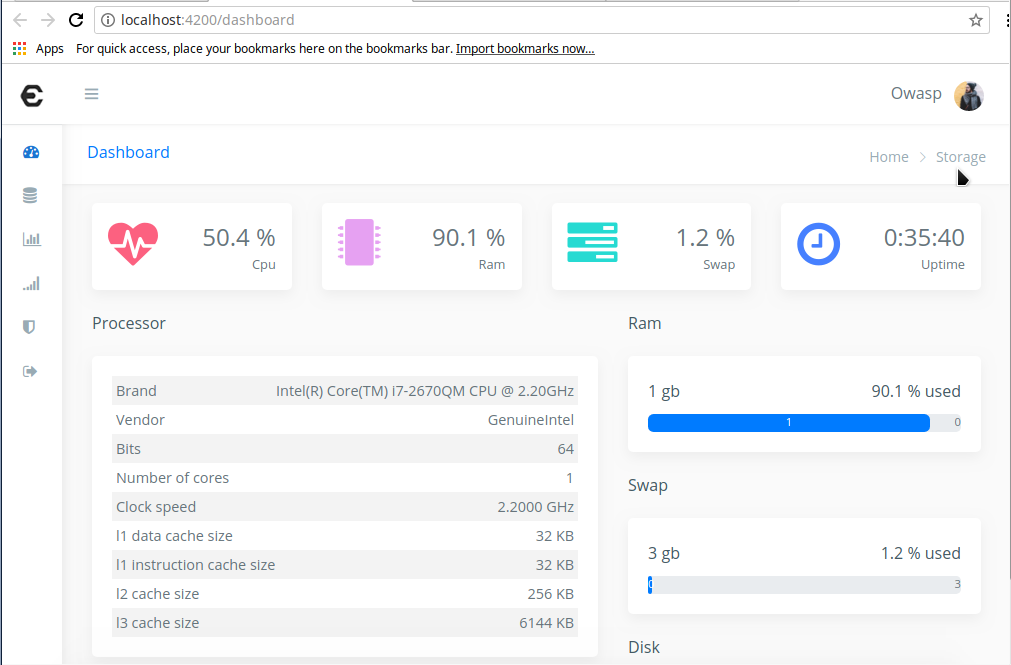
Configuring using Web UI
Starting Firewall
Usage:
sudo SecureTea.py --interface <data> --inbound_IP_action <data> --inbound_IP_list <data> --outbound_IP_action <data> --outbound_IP_list <data> --protocol_action <data> --protocol_list <data> --scan_action <data> --scan_list <data> --dest_port_action <data> --dest_port_list <data> --source_port_action <data> --source_port_list <data> --HTTP_request_action <data> --HTTP_response_action <data> --dns_action <data> --dns_list <data> --time_lb <data> --time_ub <data>
Starting AWS-SES
Usage:
sudo SecureTea.py --aws_ses <data> --aws_email <data> --aws_access_key <data> --aws_secret_key <data>
Firewall
SecureTea Firewall currently uses the following rules to filter the incoming traffic:
Process 1 (Firewall Engine):
- Filter packets based on:
- Inbound IP rules
- Outbound IP rules
- Source port rules
- Destination port rules
- Protocols
- Scan for downloads in HTTP websites
- DNS filter rules
- Filter HTTP request & response
- IP packet first fragment
- IP packet fragment boundary
- IP packet fragment small offset
- Unknown IP version
- Invalid IP source
- Invalid IP header length
- Network congestion detection
- Ending FIN-ACK handshakes
- TCP Packet with None flag
- SYN fragmentation
- ICMP fragmentation attack
- Large ICMP packets
Apart from that, the background process deals with the following functions:
Process 2 (Firewall Monitor):
- Monitor open ports
- Monitor active services
- Monitor network usage
- Monitor active CPU process
Intrusion Detection System
SecureTea Intrusion Detection System (IDS) deals with the following attack vectors and logs any abnormalities:
Detect probe (reconnaissance) attacks (performed for information gathering)
- General scans: TCP ACK & TCP Window, UDP, ICMP scans
- Stealth scans: FIN, XMAS, NULL scans
- OS fingerprinting scans
Detect Denial of Service (DoS) & Remote to Local (R2L) attacks
- DoS attacks
- CAM Table Exhaustion
- DHCP Exhaustion
- Man in The Middle (MiTM) / ARP cache poisoning
- SYN flood attack
- Ping of death
- Land attack
- Wireless
- Deauthentication attack
- Hidden node attack
- SSID spoofing
- Fake access point
Generate report about the malicious IP address using OSINT tools The report will contain the following fields:
- Reverse DNS
- Geo lookup
- WHOIS lookup
- Other important details
Running Intrusion Detection System
Insecure Headers
Check/monitor the website for the followings:
- X-XSS-Protection
- X-Content-Type
- Strict Transport Security
- Content Security Policy
- X-Frame
- HTTP methods
- Test all methods - ‘GET’, ‘POST’, ‘PUT’, ‘DELETE’, ‘OPTIONS’, ‘TRACE’, ‘TEST’
- Cross Site Tracing vulnerability
- Check for cookie details
System Log Monitor
System log aggregator to disparate log files, organize the useful data and apply intelligence to detect intrusion activities.
a. Log file : /etc/passwd & /etc/shadow
- Detect backdoors
- Detect user existing without a password that may lead to privilege escalation
- Check integrity of system’s password storing
- Detect non-standard hashing algorithm used in passwords to guess system manipulation
b. Log file: /var/log/auth.log & /var/log/faillog
- Detect system login attempts
- Detect password brute-force
- Detect harmful commands executed as root
- Detect port scans
- Detect SSH login attempts & brute-force
c. Log file: /var/log/syslog
- Detect malicious sniffer by extracting PROMISC mode
Server Log Monitor
System log aggregator to disparate server log files, organize the useful data and apply intelligence to detect intrusion activities.
Currently, the server log monitor supports the following log file types:
- Apache
- Nginx
The following suspicious activities/attacks can be detected:
- Attacks
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
- Cross site scripting (XSS) injection
- SQL injection (SQLi)
- Local file inclusion (LFI)
- Web shell injection
- Reconnaissance attacks
- Web crawlers / spiders / bots
- URL Fuzzing
- Port scans
- Bad user agents
-
Log bad/suspicious IP (later on picked up by Firewall to block incoming request from that IP)
- User defined rules:
- Filter based on selected IPs
- Filter based on response code
AntiVirus
SecureTea real-time signature & heuristic based antivirus.
The following features are currently supported:
-
Auto fetch updates: Smart update mechanism, that keeps track of the last update and resumes update from the last downloaded file. User can configure to switch off and switch on the auto-update feature.
-
Real-Time monitoring: Scan as soon as a file is modified or a new file is added.
- Scanner engine: Scanner engine runs on 3 process, they are as follows:
- Hash Signature scanner
- Yara Heuristic scanner
- Clam AV Scanner
- YARA rules can detect:
- Viruses
- Worms
- Ransomware
- Adware
- Spyware
- Rootkits
- RATs
-
Leveraging the power of VirusTotal API: Optional for users, provides an easy option for them to test for specific files against multiple anti-viruses & in a safe sandbox environment, i.e. after a file is detected malicious, the file will be put under VirusTotal test for a final confirmation.
-
Monitor orphaned files: Use SUID, SGID and read capabilities in Linux to separate orphaned files and check if any file is granted more capabilities than it should be.
-
Keeps an eye on USB devices: Start scanning the USB device as soon as it is plugged in & report for any virus/malware found.
-
Cleaning the found files: Opt for either auto-delete or manual delete option, in auto-delete the file found malicious is automatically deleted, whereas in manual it requires the confirmation of the user.
- Custom and Full scan options
Web Deface Detection
Monitor server files to detect any changes, roll back to default in case of defacement.
Features:
-
Auto locate the server files based on the user choice of server (i.e. Apache, Nginx, etc.) and the operating system detected.
-
Allow user to overwrite the above default auto-located file path and use their custom file path.
-
Scan the directory for files and generate a cache / backup of the files.
-
Generate SHA 256 hashes of each file and use them for comparison.
SecureTea Web Defacement Detection would detect file addition, deletion and modification and roll back to the original file immediately. It would not allow addition of any new files, deletion of files or any type of modification to the current existing files.
IoT Anonymity Checker
“Shodan is a search engine which collects the information about all IPv4 and IPv6 devices connected to the internet and gives us the ability to search devices using filters that can be very sophisticated.” (source: https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/shodan-iot-problem/#gref)
In short, Shodan is a search engine for IoT devices, that can index thousands of IoT devices connected to the internet. At times, this can be great for hackers trying to gain access to the device. As a security feature, it would be good to stay out of Shodan search radar. It will good to check whether the IoT device is under the Shodan grid or not, if yes, immediate action needs to be taken or else we are all fine!